Vector decomposition
Vector decomposition refers to decomposing a vector of Rn into several vectors, each linearly independent (in mutually distinct directions in the n-dimensional space).
Vector decomposition in two dimensions
In two dimensions, a vector can be decomposed in many ways. In the Cartesian coordinate system, the vector is decomposed into a portion along the 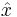 or
or 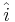 and the
and the 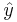 or
or 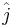 directions.
directions.
One of the most common situations is when given a vector with magnitude and direction (or given in polar form), it can be converted into the sum of two perpendicular vectors (or converted to a Cartesian coordinate).
Application in physics
Vector decomposition is used in physics to help adding vectors and hence solve many mechanical problems involving force, work, momentum, etc.
See also
- coordinate system
- Helmholtz decomposition (decomposition of a vector field)